User Guide
NUS Module Planner is a desktop app for NUS students to manage and plan the modules to enrol in upcoming semesters, optimized for use via a Command Line Interface (CLI) while still having the benefits of a Graphical User Interface (GUI). If you can type fast, NUS Module Planner can get your module planning done faster than traditional GUI apps.
Quick start
-
Ensure you have Java
11or above installed in your Computer. -
Download the latest
moduleplanner.jarfrom here. -
Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for your AddressBook.
-
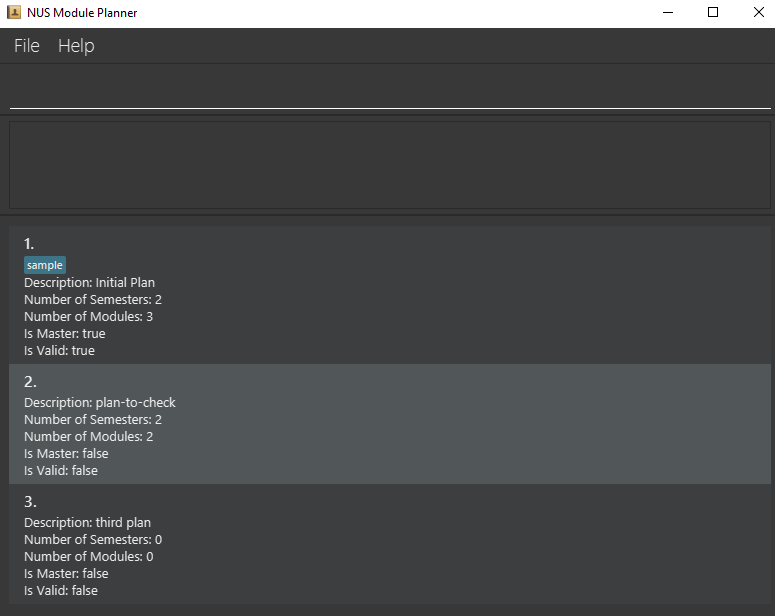
Double-click the file to start the app. The GUI similar to the below should appear in a few seconds. Note how the app contains some sample data.
-
Type the command in the command box and press Enter to execute it. e.g. typing
helpand pressing Enter will open the help window.
Some example commands you can try:-
list: Lists all plans. -
addp d/sample plan: Adds a plan with descriptionsample planto the Address Book. -
deletep p/3: Deletes the 3rd plan shown in the current list. -
clear: Deletes all plans. -
exit: Exits the app.
-
-
Refer to the Features below for details of each command.
Features
![]() Notes about the command format:
Notes about the command format:
-
Words in
UPPER_CASEare the parameters to be supplied by the user.
e.g. inaddp d/DESCRIPTION,DESCRIPTIONis a parameter which can be used asaddp d/Networking Focus Area. -
Items in square brackets are optional.
e.gd/planDesc [t/TAG]can be used asd/planDesc t/3 years. -
Items with
… after them can be used multiple times including zero times.
e.g.[t/TAG]…can be used as ` ` (i.e. 0 times),t/3 years,t/3 years t/2 internshipsetc. -
Parameters can be in any order.
e.g. if the command specifiesp/PLAN_NUMBER s/SEM_NUMBER,s/SEM_NUMBER p/PLAN_NUMBERis also acceptable. -
If a parameter is expected only once in the command but you specified it multiple times, only the last occurrence of the parameter will be taken.
e.g. if you specifyd/myplan1 d/myplan2, onlyd/myplan2will be taken. -
Extraneous parameters for commands that do not take in parameters (such as
help,list,exitandclear) will be ignored.
e.g. if the command specifieshelp 123, it will be interpreted ashelp.
Viewing help : help
Shows a message explaining how to access the help page.
Format: help
User Commands
General Commands
Check graduation : validate
Format: validate
Note: The validate command checks if a plan is valid by looking at whether or not the modules contained in its history match those of the current
master. Hence,masteris always valid. The command does not check for pre-requisites and preclusions with this release.
Example: if master is at current semester
2, all other plans have their semester1s checked, if these semester1s match the master module, the plan is valid.
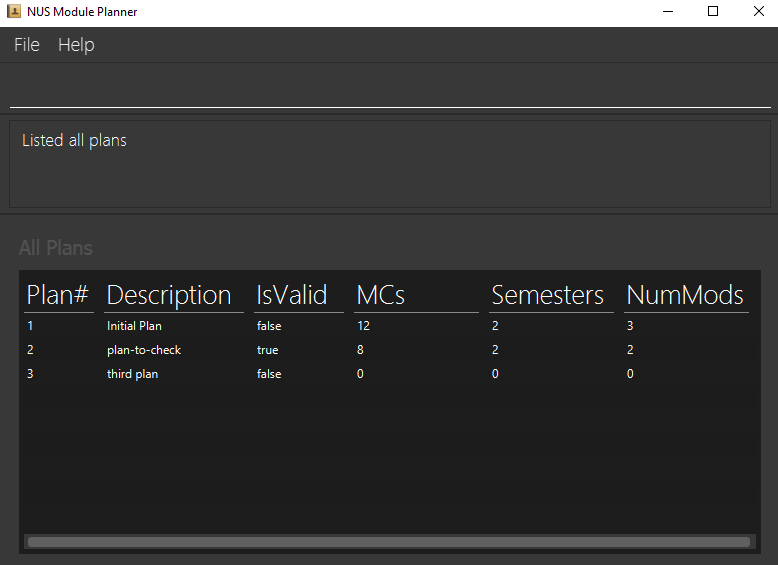
- Shows header
- Shows plan number
- Shows description of plan
- Shows if the plan is valid compared to master plan
- Shows how many MCs the plan has
- Shows how many semesters the plan has
Clearing all entries : clear
Clears all entries from the address book.
Format: clear
Exiting the program : exit
Exits the program.
Format: exit
Plan commands
List a summary of all plans: list
Format: list
This command must be done by the user at least once before they can use other commands. Marks the given plan as the master plan, and this plan should contain all the modules that the user has taken (if any).
Example output:
Create/Delete Plan: addp/deletep
Format for adding: addp d/DESCRIPTION [OPTIONAL: t/TAG...]
Format for deleting: deletep p/PLAN_NUMBER
Shows 2 rows:
- Whether the plan is added/deleted successfully/unsuccessfully
- Plan number
Constraints:
- Trying to add a plan with invalid description will not be allowed
- Trying to delete a plan that does not exist will not be allowed
- Tags provided when adding a plan should contain only alphanumeric characters with no spaces
Example output for adding plan:
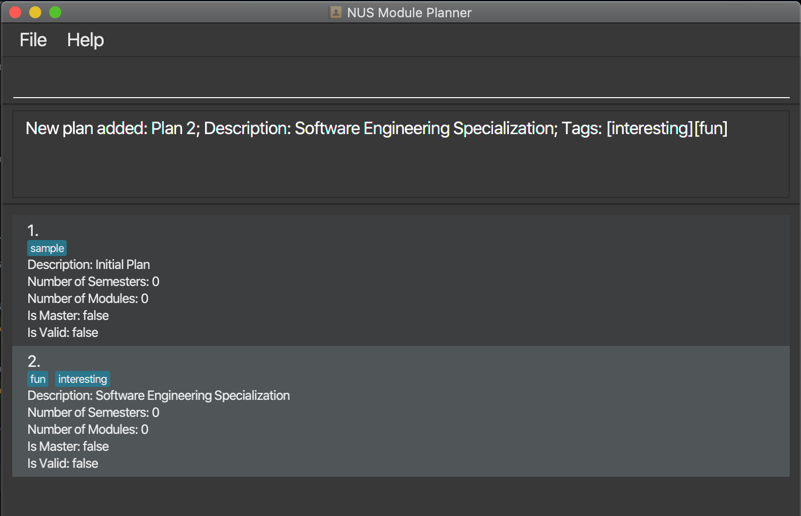
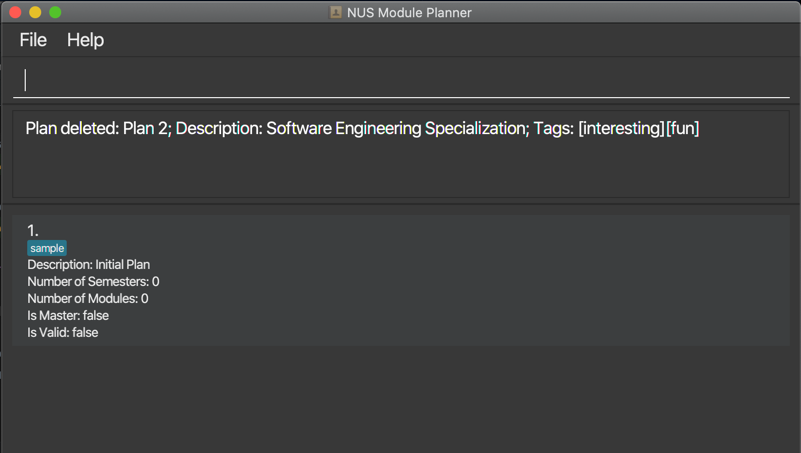
Example output for deleting plan:
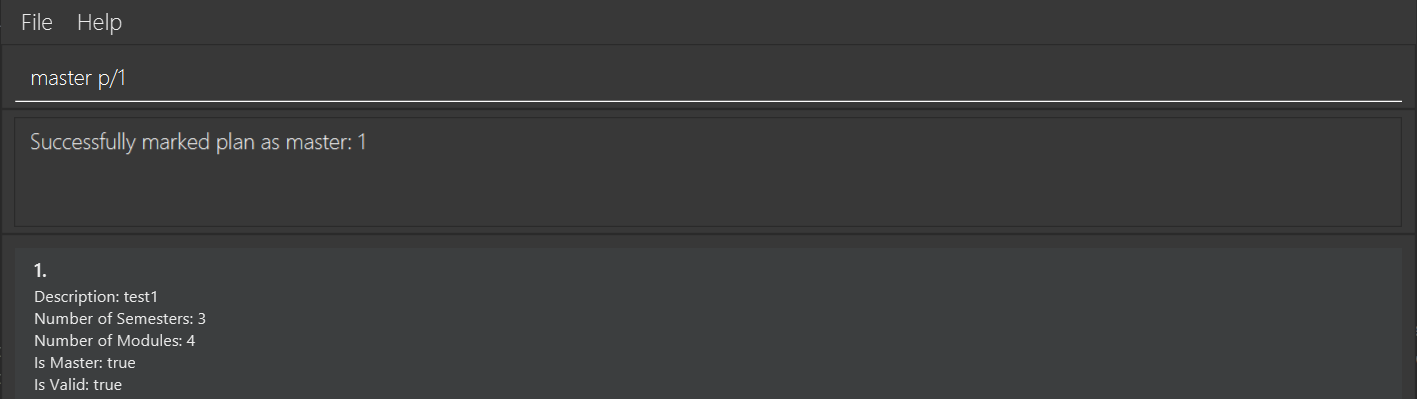
Set Plan as Master Plan: master
Format: master p/PLAN_NUMBER
This command must be done by the user at least once before they can use other commands. Marks the given plan as the master plan, and this plan should contain all the modules that the user has taken (if any).
Example output:
Semester commands
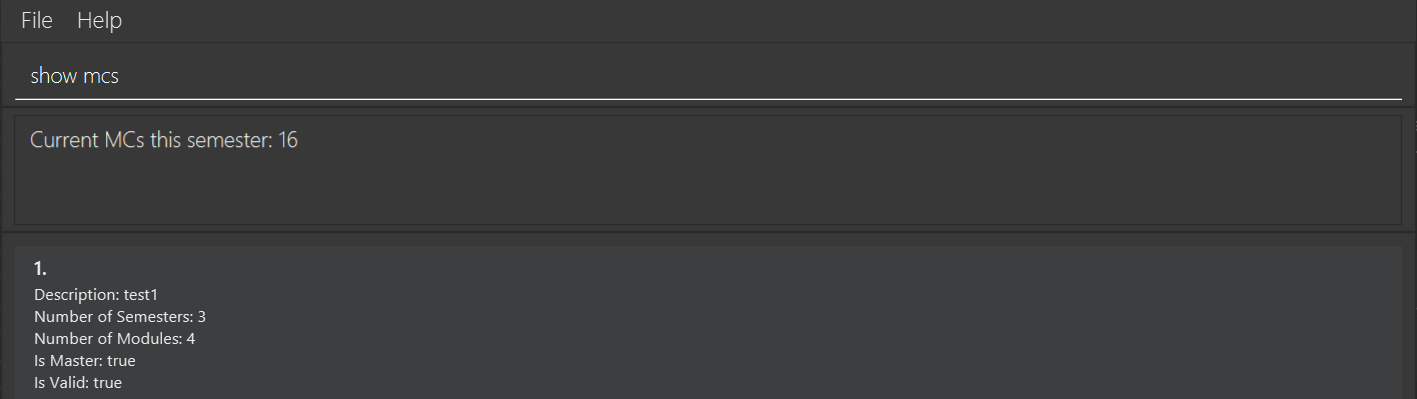
Show the number of MCs the user is currently taking: show MCs
Format: show mcs
Example output:
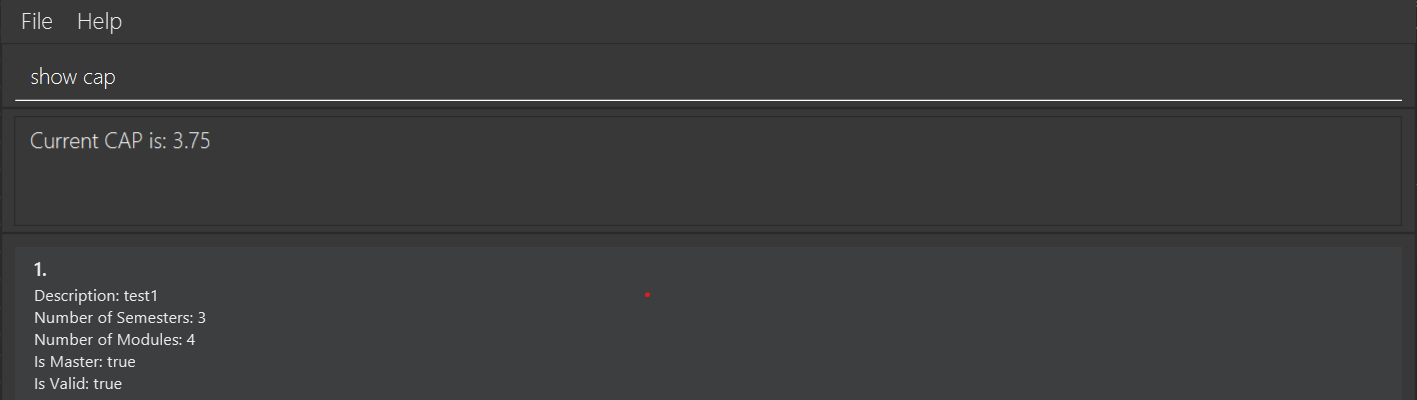
Calculate and show the current CAP (Cumulative academic points) of the student: show cap
Format: show cap
This command takes in the grades of modules user has marked as completed and entered their grade, and calculate their CAP using this formula:

Example output:
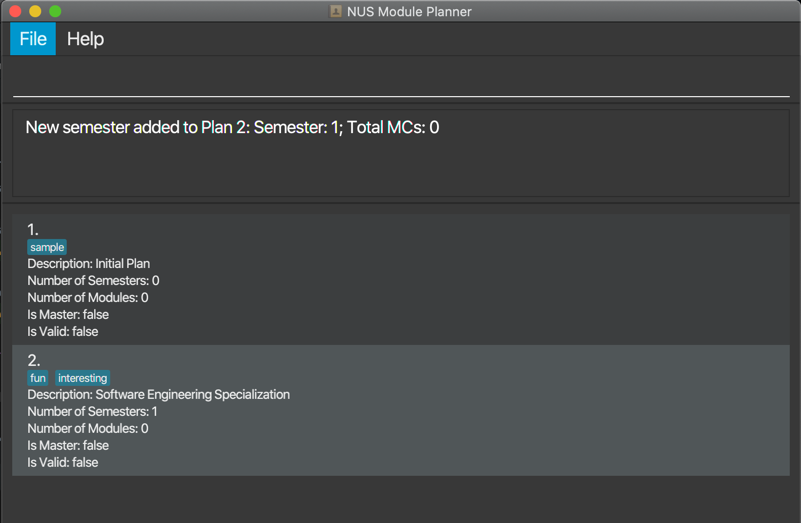
Add/Delete Semester to/from Plan: adds/deletes
Format for adding: adds p/PLAN_NUMBER s/SEM_NUMBER
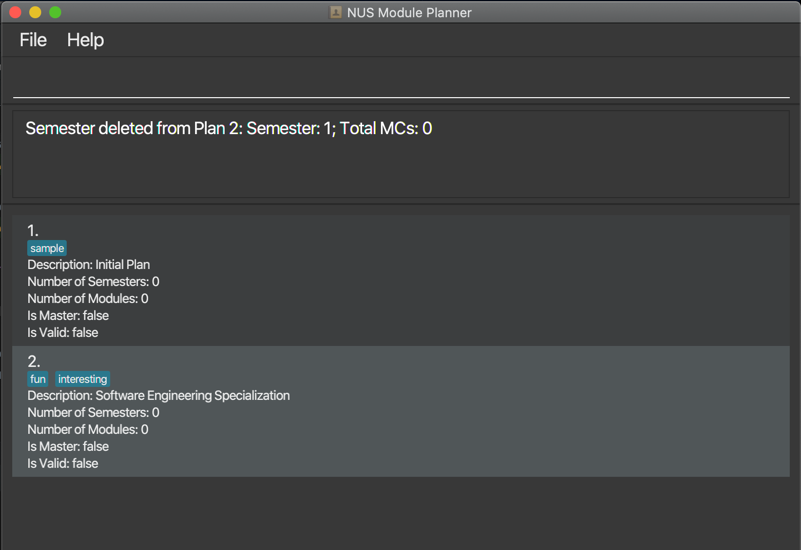
Format for deleting: deletes p/PLAN_NUMBER s/SEM_NUMBER
The output will show whether the operation was successful and include the semester number in its output.
Constraints:
- Trying to add a semester that already exist will not be allowed
- Trying to delete a semester that does not exist will not be allowed
- A semester number must be a positive integer
Example output for adding semester:
Example output for deleting semester:
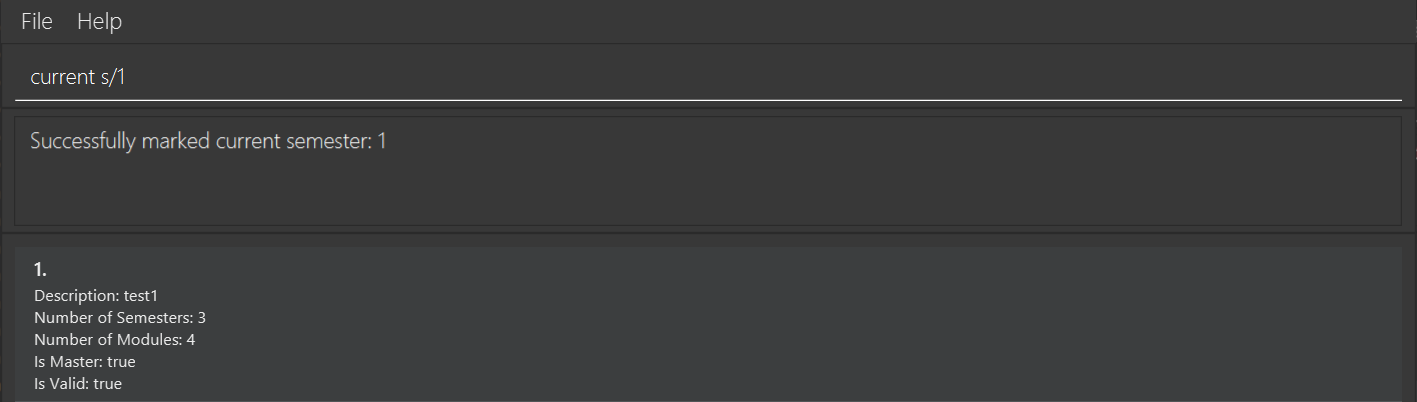
Set Semester as in-progress: current
Format: current s/SEM_NUMBER
Marks the supplied semester as the current semester of the master plan. This indicates that all previous semesters are part of the user’s history and all future semesters have yet to be attempted. The user will have to manually update the current semester as time progresses.
Example output:
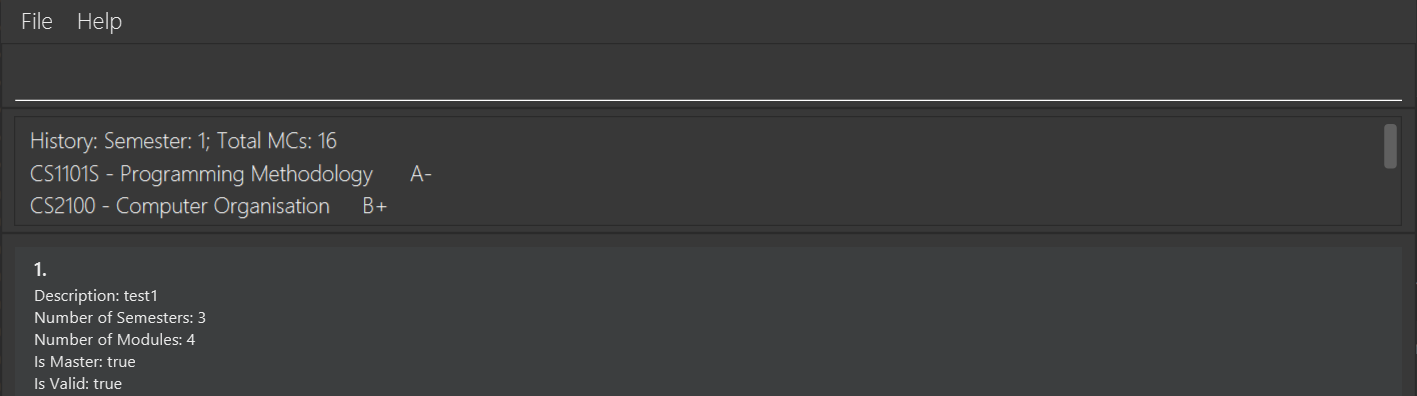
Show history: history
Format: history
The above command takes no arguments and shows the user a list of modules that they have completed up until before the current semester.
Tip: The current semester is the semester that was marked using the
current semestercommand.
Example output:
Module commands
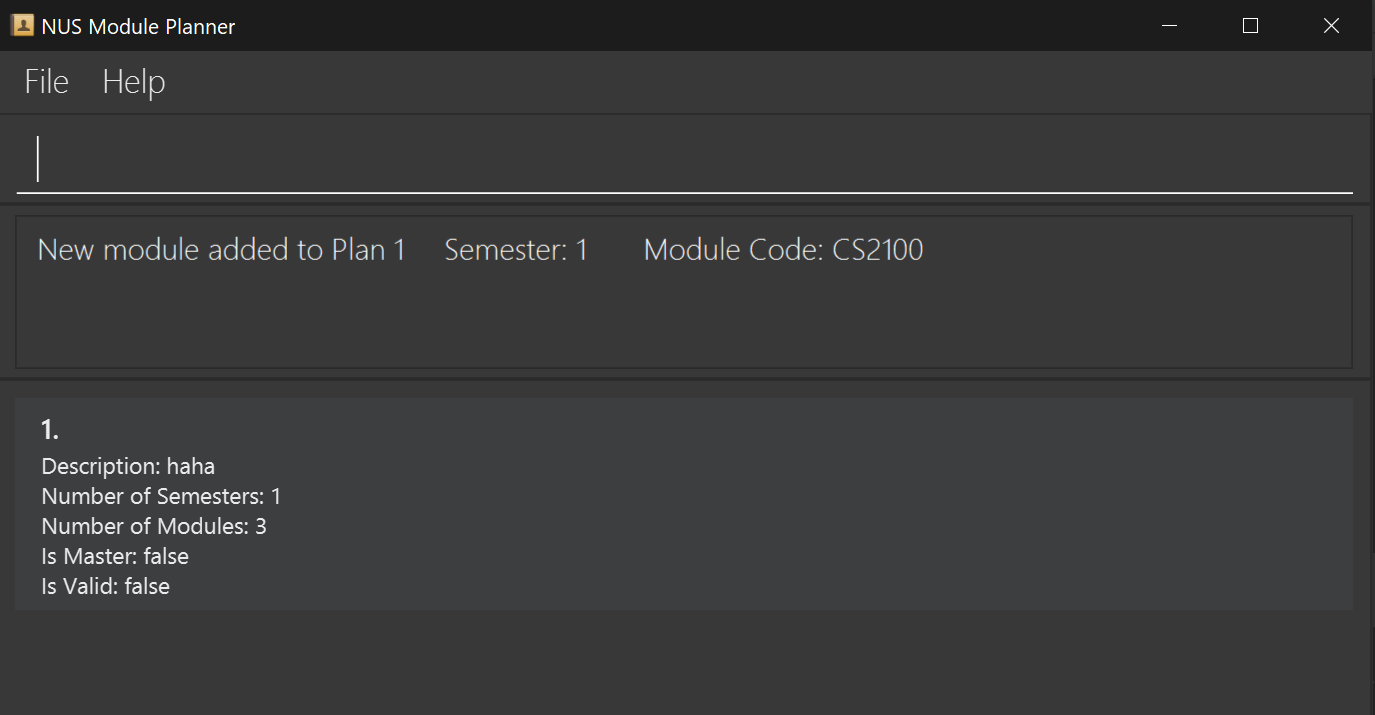
Add/Delete module to/from semester: addm/deletem
Format for adding: addm m/MODULE_CODE p/PLAN_NUMBER s/SEM_NUMBER
Format for adding module with grade: addm m/MODULE_CODE p/PLAN_NUMBER s/SEM_NUMBER g/GRADE
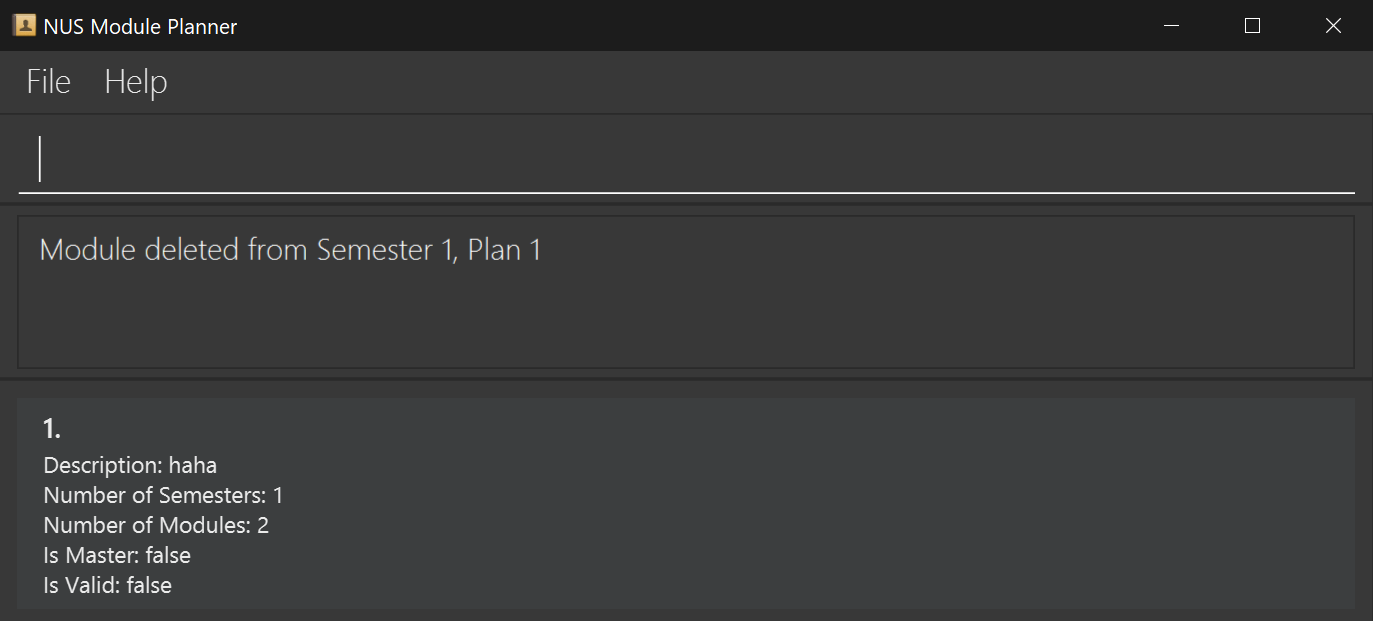
Format for deleting: deletem m/MODULE_CODE p/PLAN_NUMBER s/SEM_NUMBER
SEM_NUMBER here references to the semester number of the semester user created.
For example, if user added a semester using adds p/1 s/5, to add module to this semester user need to use addm p/1 s/5 m/MODULE_CODE
Tip: A user can view module info to see more details about it. (See
info)
This command takes in three arguments, MODULE_CODE, PLAN_NUMBER and SEM_NUMBER, and outputs meta details about the module being added/deleted, as well as whether the addition/deletion was successful or not.
The details to output are as follows:
- Module addition/deletion success status
- Semester number
- Module code
Constraints:
- Trying to add a module that already exists will not be allowed
- Trying to add/delete a nonexistent module code/plan number/semester number will not be allowed
Note: As this is not a fully fledged production level project, there are limited modules for users to add. If in the future this project grows to a production piece, it will use relevant NUS APIs to collect modules for users to add. Instead, currently there are only dozens of modules for users to add, but for the purposes of testing and showcasing this product, it is sufficient.
Example output for add module command:
Example output for deleting a module:
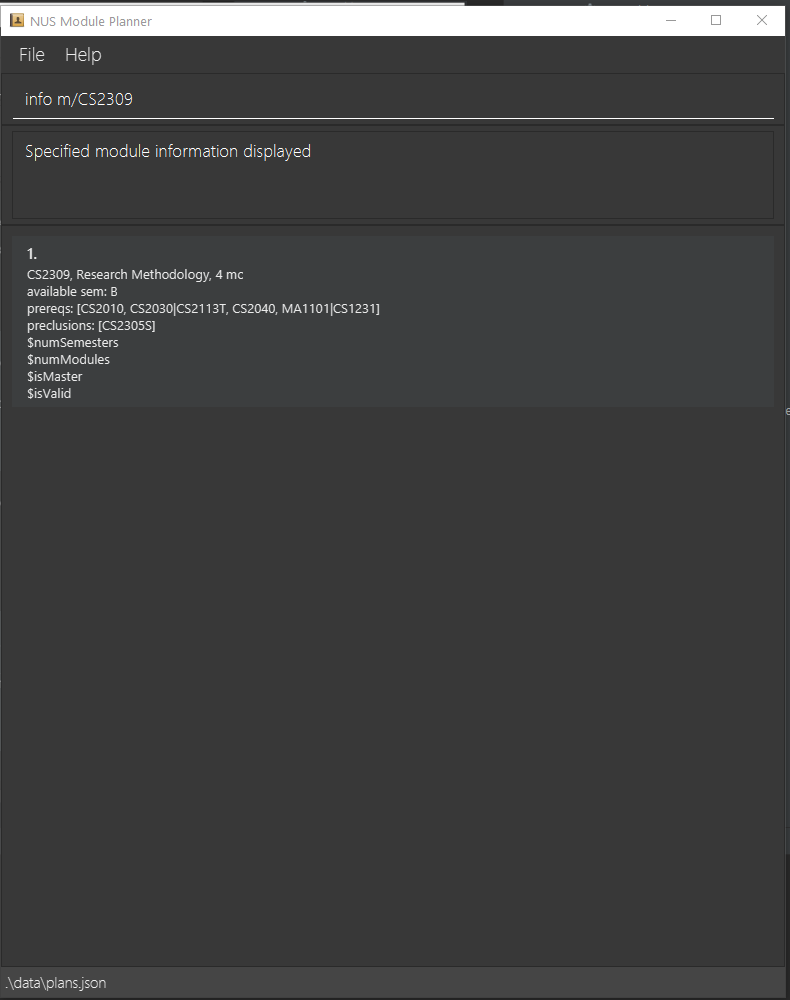
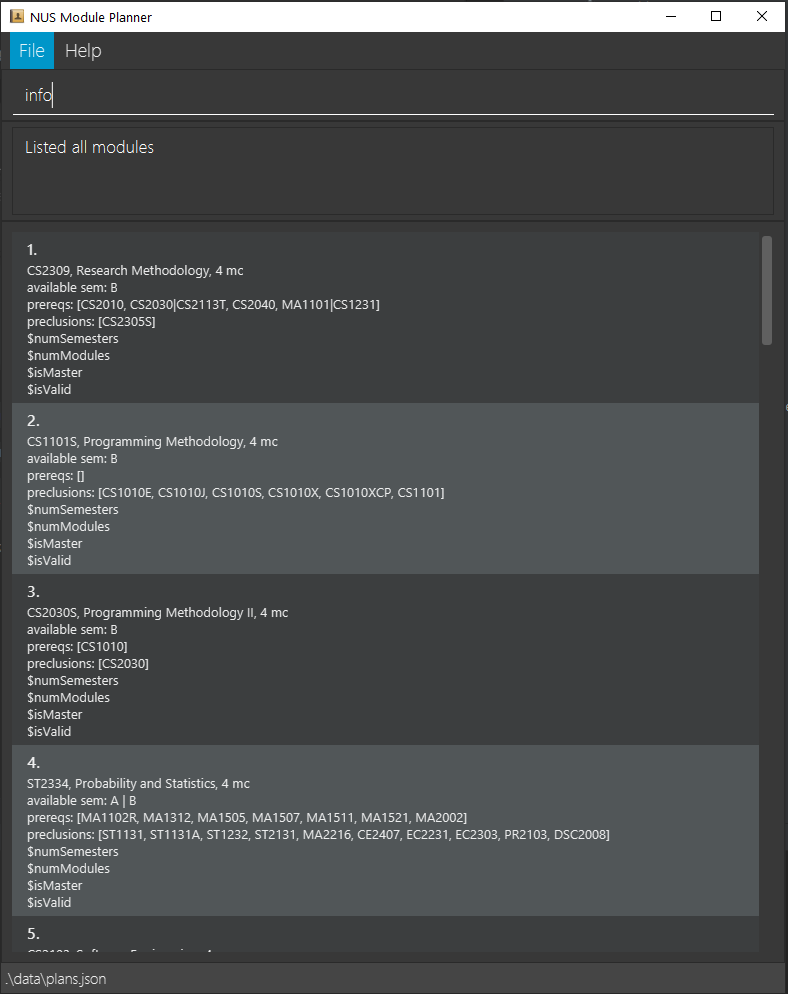
View module info: info
Format: info m/MODULE_CODE
Tip: A user can also add a module to a plan/semester (See
add/delete)
By default, this command takes in one optional argument, MODULE_CODE and outputs the module information including:
- Brief Description
- Number of MCs
- Semesters available
- Pre-requisites
- Preclusions
Constraints:
- Module has to exist
Example output listing all module information:
Example output for finding a specific module information
Overall input constraints
The NUS Module Planner app is designed to help students track their typical study plans. Hence, user inputs for indexes such as plan numbers or semester numbers are only guaranteed to work within reasonable limits. For example a student should never have 2 billion semesters in their study plan as this would exceed the typical human lifetime.
Explicitly, the following should take on values between 1 and 100 only. Correct behaviour of the app is not guaranteed beyond these bounds.
- Semester number
- Plan number
- Number of modules in a plan or semester
Please note that if you manually edit the moduleinfo.json or the plans.json files that the NUS Module Planner application may not longer function as expected.